A brainless, one-celled organism with a knack for acquiring meals is serving to astronomers review the largest, most mysterious structure in the universe — the cosmic website. But, very first, points could get a bit slimy.
The cosmic website is a wide network of interconnected filaments made of dim make a difference and gas that types the scaffolding the whole universe is constructed upon. These filaments can extend hundreds of thousands and thousands of mild-a long time, and they hook up galaxies, galaxy clusters and even galaxy superclusters. On the other hand, due to the fact the cosmic website is extremely faint — and the dim make a difference in just it doesn’t interact with mild — it is exceptionally hard to map.
To deal with this problem, researchers at the College of California, Santa Cruz, sifted by archived data for extra than 37,000 galaxies prior to charting their positions in the sky. They then utilised a complex algorithm to map out the invisible filaments of gas and dim make a difference concerning those galaxies to ascertain how they are interacting with each individual other, as very well as how the cosmic website influences star formation in these galaxies.
But this wasn’t your normal algorithm. Rather, the researchers utilised a model inspired by slime mould — specially, the species Physarum polycephalum.
This algorithm mimics the mold’s meals-in search of conduct, which sends out tendrils of reconnaissance mould to hunt for nearby meals. If a particular mould thread stumbles on meals, it thrives, developing a powerful link concerning the meals and the rest of the colony.
So by substituting personal galaxies for the mould-based mostly algorithm’s “food,” researchers ended up capable to create a 3D map that implies how the galaxy-connecting filaments of the cosmic website are intertwined.
Incidentally, the gas concerning galaxies also acts as a sort of “cosmic food” that fuels star formation. And the moment you know how cosmic website filaments are related to a galaxy, you can hazard a guess at the charge at which the galaxy is — or is not — forming stars. These types of a prediction is based mostly on whether or not or not a galaxy is related to the cosmic website, as very well as how tightly certain it is to other galaxies. If it is related also strongly, it runs the threat of drying up chances for star formation also loosely, and it just can’t get to plenty of fuel.
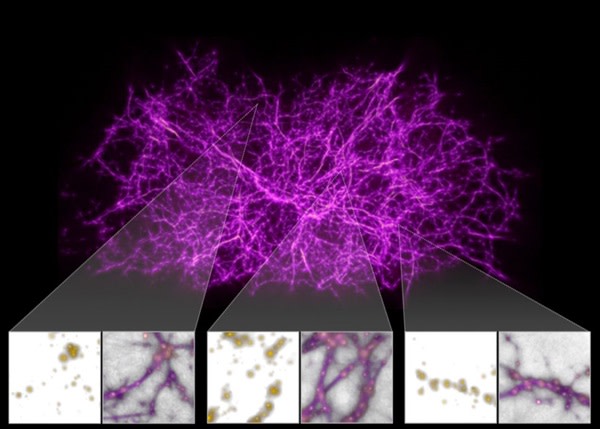
Researchers seeded an algorithm inspired by the meals-in search of conduct of slime mould with the positions of about 37,000 galaxies, the place the galaxies served as the “food.” This assisted them model and produce a 3D map of the cosmic website connecting these galaxies. Over, the galaxies (or meals) are shown in yellow, even though the cosmic website is shown in purple. (Credit rating: NASA/ESA/J. Burchett and O. Elek/UC Santa Cruz)
From Slime to Room
The notion to use a slime-based mostly algorithm to map the cosmic website arrived from co-author Oskar Elek, a UC Santa Cruz computational media publish-doc. He had beforehand observed the get the job done of slime mould algorithms, so he urged Joe Burchett — an astronomer at UC Santa Cruz and lead author of the new paper — to apply it to his get the job done on the cosmic website, whose structure continues to be elusive.
“He actually sent me screen shots of the data fitted with this remaining algorithm,” Burchett states. “What I observed was a trace of the reconstruction of the cosmic website that appealed a lot, a lot, a lot extra to my intuitive sense of what the cosmic website really should appear like [when compared with past designs].”
This is not the very first time scientists have utilised slime molds to map many structures. Slime molds are expert filament builders, developing sophisticated underground networks that enable them lookup for meals and methods. These one-celled organisms get the job done as a single substantial colony that can be up to one foot in diameter. And, oddly, their filamentary structures present a propensity for what could be described as trouble-fixing.
Slime molds are adept at “shortest path” complications, these types of as acquiring the most effective way to weave by a maze to identify meals hidden in just. It is been referred to as “slime mould computing” prior to, and even likened to a rudimentary intelligence — however this clearly will come with its personal subset of thorny concerns.
“For a slime mould, the environment is a mix of two fields: gradients of attractants [stuff it wants] and gradients of repellents [stuff it avoids],” Andrew Adamatzky, a professor in unconventional computing at the College of West England, wrote in an e mail. “The slime mould merely follows the gradients. This is how it calculates, for example, the shortest path.”
By monitoring how the slime mould algorithm related separate galaxies, researchers realized the place to appear for cosmic website filaments in archived observations. “Wherever we observed a filament in our model,” Burchett reported in a statement, “the Hubble spectra showed a gas signal, and the signal obtained more powerful toward the center of filaments the place the gas really should be denser.” This usually means the researchers not only utilised the algorithm to efficiently pinpoint the place threads of the cosmic website really should be, but also actually find them.
“For the very first time now, we can quantify the density of the intergalactic medium from the distant outskirts of cosmic website filaments to the hot, dense interiors of galaxy clusters,” Burchett reported. “These success not only validate the structure of the cosmic website predicted by cosmological designs, they also give us a way to strengthen our being familiar with of galaxy evolution by connecting it with the gas reservoirs out of which galaxies variety.”
The new research was released March ten in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
